Difference between revisions of "Lpe-blueprint"
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
blocked at the active level, or runs to its end) | blocked at the active level, or runs to its end) | ||
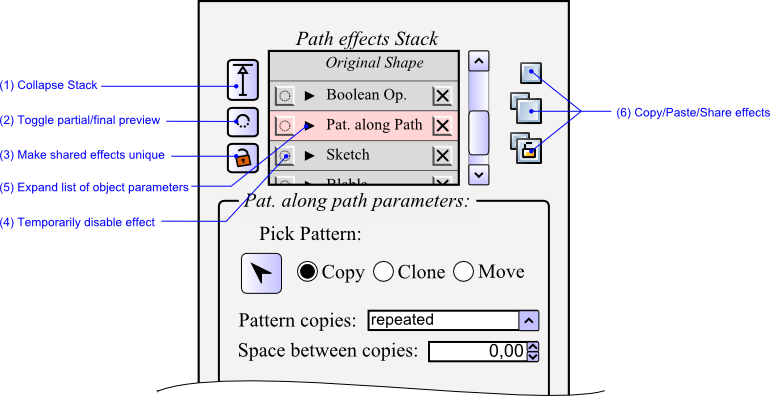
*The stack can be collapsed from the active effect to the original shape. The output of the active effect becomes the new original shape. | *The stack can be collapsed (1) from the active effect to the original shape. The output of the active effect becomes the new original shape. | ||
*Each effect can be temporariliy bypassed to save performance and interactivity | *Each effect can be temporariliy (4) bypassed to save performance and interactivity | ||
*Effects can be draged and droped to reorganize the stack | *Effects can be draged and droped to reorganize the stack | ||
*Effects can copied, pasted, cloned (i.e. shared) between objects. Shared effects can be made unique. | *Effects can copied, pasted, cloned (i.e. shared) between objects (6). Shared effects can be made unique (3). | ||
*Effects names (i.e. svg id attribute) can be edited. | *Effects names (i.e. svg id attribute) can be edited. | ||
Revision as of 21:36, 24 February 2008
'Live path effects' blue print proposal.
Here are some propositions about what the future of live path effects could look like in the future, from the features/UI point of view. The goal is not to require this or that particular feature, but to have an idea about what could be done, what is hard, what is easy, what is worth and what is not, list possible alternatives, etc...
It is natural to use several successive live path effects on the same object, leading to an effect stack. The proposition below mimics the modifier stack found in most 3D software.
Effect stack: features and UI
General usage
A side panel is dedicated to the effect stack. On the top is displayed the stack itself, and below the parameters of particular effects. The picture below summerizes the main features of the stack area.
A side panel is dedicated to the effect stack. On the top is displayed the stack itself, and below the parameters of particular effects. The picture below summerizes the main features of the stack area.
The full stack can be navigated and any effect in the stack can be selected to become active. The pannel below the stack displays the active effects parameters. In the main window (the canvas), the output of the active effect is displayed (ideally, a button near the stack toggles wether the stack is blocked at the active level, or runs to its end)
- The stack can be collapsed (1) from the active effect to the original shape. The output of the active effect becomes the new original shape.
- Each effect can be temporariliy (4) bypassed to save performance and interactivity
- Effects can be draged and droped to reorganize the stack
- Effects can copied, pasted, cloned (i.e. shared) between objects (6). Shared effects can be made unique (3).
- Effects names (i.e. svg id attribute) can be edited.
Some effect use other objects (paths, groups...) as parameters. In this case, the line of the effect in the stack can be expanded to show the list of all object parameters (see fig. 2).
As such objects might be "virtual" (i.e. not available on the canvas) and complex (typically groups of objects carrying effects on their own), an edit mode is needed for such objects that goes beyond the node editor: all operations (style, z-order, path effects...) should be availble.
To this end, selecting an object parameter in the effect stack enters edit mode for that object: its own effect stack is inserted in the global stack(bracketed with easily identified color), and each level of it can be edited normally (in particular, deeper object parameters might be recursively edited).
Edit mode exits when the effect is not active anymore, i.e.
- another object parameter is selected,
- the list of object parameters is closed,
- another effect is selected,
- the object is deselected.
(for convenience, a level in the stack could be pined, to avoid non intentional exits).
Generic effect: features and UI
This section describes the general features desired for lpes.
- use any object as input(s): groups, clones, text...
- check restrictions for input, and eventually warn the user (eg. accept only connected paths...)
- object paramters are picked with the mouse, and copied, cloned, or moved into the effect according to user choice (see fig. 1).
- be aware of the style of the inputs.
- can output full svg data
- can recieve an extra selection of the input (a list of objects, path componenents or nodes of the input) to restrict the effect to this selection, see "Selector" effect below.
Particular effects: propositions of new effects
Boolean operation
Non destructive operation are usefull. No particular comment.
Transform effect
Applies a transform matrix to the object; automatically added before a new effect if the object has a non empty transform attribute. This is needed since transforms and effects do not commute in general...
Style effect
Applies a given style to the object; added automatically when a new style is applied to an object with non empty stack. Usefull to overwrite the default style produced by other effects. Should allow to set the priority of each style component (replace old style, replace only if not set...)
Selector
This effects selects a part of the input. It has 3 modes:
- object level: selects object(s) within a group.
- path level: selects component(s) within a path.
- [node level: selects node(s) within a path.](? --- delicate)
The subsequent effects should work on this selection, and leave everything else unchanged. (usefull to apply different effects to different step of an interpolate effect for instance)
Notice that whenever the stack is modified before this effect, the user should be warned that this modifier depends on the "topology" of the input...
Pattern along path
- Work on groups: add specifications!
- Offset parameters, space between copies.
- Option to fuse nearby ends (?)
- Option to leave the original shape in the output (?)